Shaqif Arnun on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Beaufort or Belfort Castle, known locally as Qal'at al-Shaqif ( ar, قلعة الشقيف, Qalʾāt al-Shaqīf) or Shaqif Arnun, is a Crusader fortress in
 The outcrop Beaufort occupied overlooks the
The outcrop Beaufort occupied overlooks the  The
The



 After the Ottoman conquest of Syria in 1516, the Ottomans attempted to revive the area by granting military benefices (''timar'') to Ottoman cavalry soldiers around Shaqif Arnun castle. The
After the Ottoman conquest of Syria in 1516, the Ottomans attempted to revive the area by granting military benefices (''timar'') to Ottoman cavalry soldiers around Shaqif Arnun castle. The
p. 534
p. 535
* {{Authority control Castles in Lebanon Castles and fortifications of the Kingdom of Jerusalem Nabatieh Governorate Tourist attractions in Lebanon Castles and fortifications of the Knights Templar
Nabatieh Governorate
Nabatieh Governorate ( ar, محافظة النبطية, ') is one of the nine governorates of Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in West ...
, Southern Lebanon
Southern Lebanon () is the area of Lebanon comprising the South Governorate and the Nabatiye Governorate. The two entities were divided from the same province in the early 1990s. The Rashaya and Western Beqaa Districts, the southernmost distric ...
, about to the south-south-east of the village of Arnoun
Arnoun ( ar, ارنون, Syriac-Aramaic: ܐܪܢܘܢ) is a majority Lebanese Shia village south-east of Nabatiyeh, in Nabatiyeh Governorate, southern Lebanon. The village is located approximately from the Israeli border. The village is approx ...
. There was a fortification on the site before it was captured by Fulk, King of Jerusalem
Fulk ( la, Fulco, french: Foulque or ''Foulques''; c. 1089/1092 – 13 November 1143), also known as Fulk the Younger, was the count of Anjou (as Fulk V) from 1109 to 1129 and the king of Jerusalem with his wife from 1131 to his death. During t ...
, in 1139 and construction of the Crusader castle probably began soon after. Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and ...
captured Beaufort in 1190, but 60 years later Crusaders re-took it. In 1268 Sultan Baibars
Al-Malik al-Zahir Rukn al-Din Baybars al-Bunduqdari ( ar, الملك الظاهر ركن الدين بيبرس البندقداري, ''al-Malik al-Ẓāhir Rukn al-Dīn Baybars al-Bunduqdārī'') (1223/1228 – 1 July 1277), of Turkic Kipchak ...
finally captured the castle for the Islamic forces.
Beaufort provides one of the few cases in which a medieval castle proved of military value and utility in modern warfare as well, as its late 20th-century history shows.
Name
The castle was named ''bel fort'' or ''beau fort'' ( French for "beautiful fortress") by the Crusaders who occupied the castle in the 12th century. Its Arabic name ''Qala'at al-Shaqif'' means "Castle of the High Rock" (''shqif'' is theAramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in ...
word for "high rock").
History
Medieval era
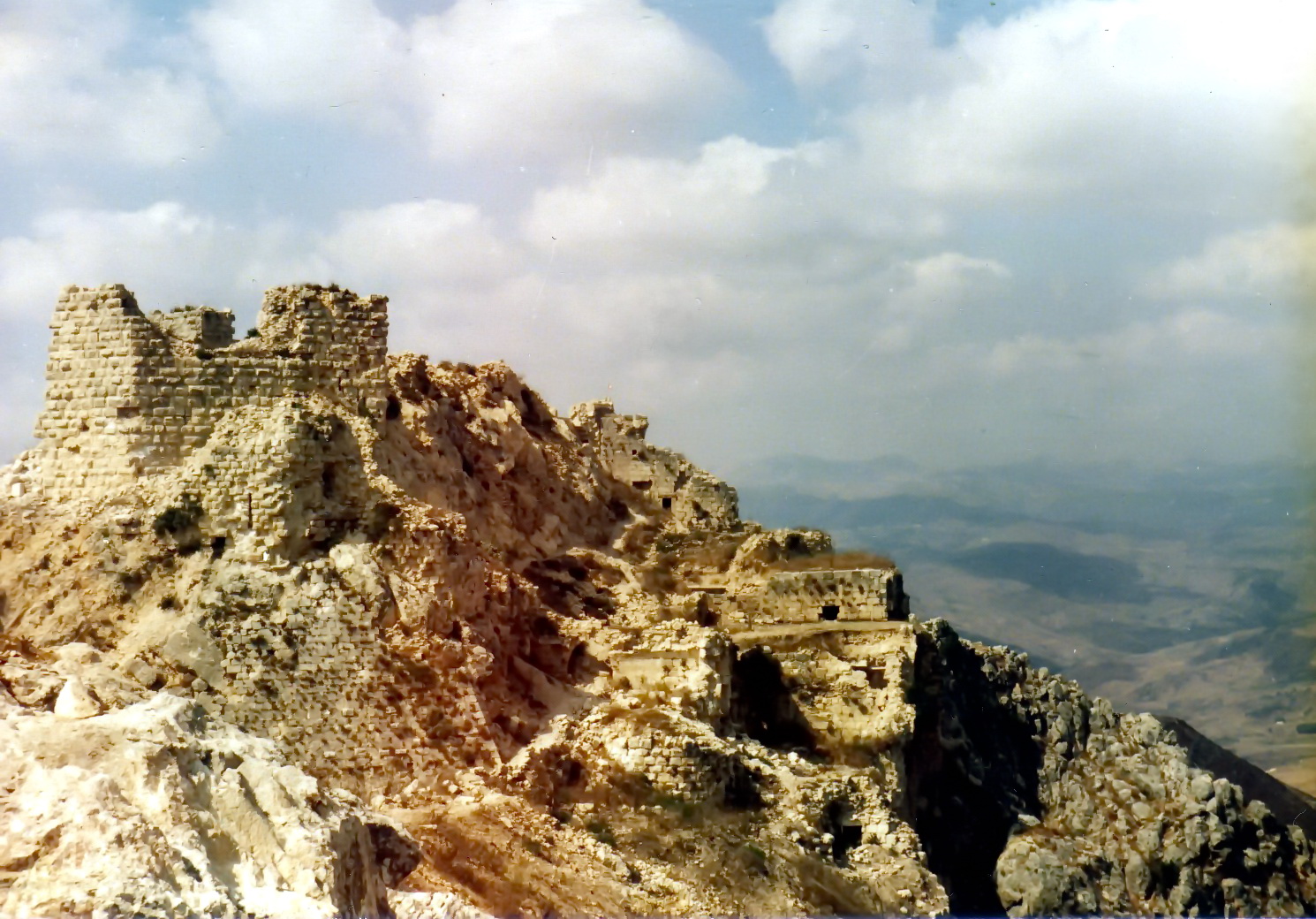
 The outcrop Beaufort occupied overlooks the
The outcrop Beaufort occupied overlooks the Litani River
The Litani River ( ar, نهر الليطاني, Nahr al-Līṭānī), the classical Leontes ( grc-gre, Λέοντες, Léontes, lions), is an important water resource in southern Lebanon. The river rises in the fertile Beqaa Valley, west of B ...
.Kennedy (1994), p. 41 The river flows past the east side of the castle, which stands atop a cliff which declines steeply to the river.Kennedy (1994), p. 43 Little is known of the site prior to its capture by Crusader forces in 1139, as no contemporary documents mention the site before then. However, historians assume that the castle's commanding hilltop site made it a strategic position that was fortified before its capture by the Crusaders.Grussenmeyer & Yasmine (2003), p. 2 Fulk, King of Jerusalem
Fulk ( la, Fulco, french: Foulque or ''Foulques''; c. 1089/1092 – 13 November 1143), also known as Fulk the Younger, was the count of Anjou (as Fulk V) from 1109 to 1129 and the king of Jerusalem with his wife from 1131 to his death. During t ...
, captured the fortification of Qal'at al-Shaqif in 1139 and gave the site to the lords of Sidon
Sidon ( ; he, צִידוֹן, ''Ṣīḏōn'') known locally as Sayda or Saida ( ar, صيدا ''Ṣaydā''), is the third-largest city in Lebanon. It is located in the South Governorate, of which it is the capital, on the Mediterranean coast. ...
. Medieval historian Hugh Kennedy
Hugh Edward Kennedy (11 July 1879 – 1 December 1936) was an Irish Cumann na nGaedheal politician, barrister and judge who served as Chief Justice of Ireland from 1924 to 1936, a judge of the Supreme Court of Ireland, Supreme Court from 1924 t ...
speculates that construction of the Crusader castle began soon after Fulk gave the site to the lords of Sidon.
 The
The Battle of Hattin
The Battle of Hattin took place on 4 July 1187, between the Crusader states of the Levant and the forces of the Ayyubid sultan Saladin. It is also known as the Battle of the Horns of Hattin, due to the shape of the nearby extinct volcano of t ...
in 1187 saw the Crusaders suffer a crushing defeat at the hands of Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and ...
. In the aftermath, many castles and cities fell to Saladin's forces so that only a handful of cities remained under the Crusaders' control. Beaufort was one of the last castles to resist Saladin. In April 1189, Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and ...
was preparing to besiege the castle and Arab sources describe the event in detail. At the time Beaufort was under the control of Reynald of Sidon who had survived the Battle of Hattin
The Battle of Hattin took place on 4 July 1187, between the Crusader states of the Levant and the forces of the Ayyubid sultan Saladin. It is also known as the Battle of the Horns of Hattin, due to the shape of the nearby extinct volcano of t ...
, While Saladin was camped at nearby Marjayoun
Marjayoun ( ar, مرج عيون: Lebanese pronunciation), also Marj 'Ayoun, Marjuyun or Marjeyoun (lit. "meadow of springs") and Jdeideh / Jdeida / Jdeidet Marjeyoun, is a Lebanese town and an administrative district, the Marjeyoun District, in ...
, preparing for the siege, Reynald met him and claimed to have Muslim sympathies. He said that while he would like to hand over control of Beaufort, his family were in the Christian city of Tyre and he could not surrender until they were safely out of the city. In the hope of a taking the castle without any bloodshed, Reynald was given three months to extract his family from Tyre; instead he used this time to repair the castle and stock up on supplies.Kennedy (1994), pp. 43–44
After three months Reynald met Saladin again, protesting he needed more time. Saladin insisted he hand over the castle immediately, so Reynald ordered the garrison to surrender. When they refused Reynald was taken prisoner and the siege began. Hostilities lasted until August that year when Saladin was forced to lift the siege to defend Acre. In April 1190 an agreement was reached where the castle's garrison would hand over control to Saladin in return for Reynald's release. The castle came under Crusader control in 1240 as part of a treaty negotiated by Theobald I of Navarre
Theobald I (french: Thibaut, es, Teobaldo; 30 May 1201 – 8 July 1253), also called the Troubadour and the Posthumous, was Count of Champagne (as Theobald IV) from birth and King of Navarre from 1234. He initiated the Barons' Crusade, was famous ...
. It was sold to the Knights Templar
, colors = White mantle with a red cross
, colors_label = Attire
, march =
, mascot = Two knights riding a single horse
, equipment ...
by Reginald's grandson, Julian of Sidon
Julian Grenier (died 1275) was the Count of Sidon from 1239 to 1260, then becoming merely titular. He was the son and successor of Balian Grenier and Ida of Reynel. He did not exhibit the wisdom of his father in his dealings with the Saracens.
...
, in 1260. In 1268, the Mamluke
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') i ...
Sultan Baibars
Al-Malik al-Zahir Rukn al-Din Baybars al-Bunduqdari ( ar, الملك الظاهر ركن الدين بيبرس البندقداري, ''al-Malik al-Ẓāhir Rukn al-Dīn Baybars al-Bunduqdārī'') (1223/1228 – 1 July 1277), of Turkic Kipchak ...
captured the castle, and there was relative calm through the 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries.
Modern era



Shiite
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, most ...
Sa'b family The Sa'b family is a prominent Shia Muslim family in Lebanon.
History
The Sa'bs were of Kurdish tribal origin and during the Ottoman era became a leading family (''zu'ama'') among the Shia Muslims of the Jabal Amil area of modern southern Lebanon ...
held the castles on the Ottomans behalf as early as 1571. In the early 17th century Fakhr-al-Din II
Fakhr al-Din ibn Qurqumaz Ma'n ( ar, فَخْر ٱلدِّين بِن قُرْقُمَاز مَعْن, Fakhr al-Dīn ibn Qurqumaz Maʿn; – March or April 1635), commonly known as Fakhr al-Din II or Fakhreddine II ( ar, فخر الدين ال ...
took the castle as a part of his network of fortifications. Fakhr-al-Din II was defeated by the Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
, who destroyed the upper portions of the castle. Thereafter it was reinvested by the Sa'bs. The area was ruled by Shiite feudal families until 1769. In 1782 the Governor of Acre
The acre is a unit of land area used in the imperial
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imp ...
, Jazzar Pasha
Ahmad Pasha al-Jazzar ( ar, أحمد باشا الجزّار; ota, جزّار أحمد پاشا; ca. 1720–30s7 May 1804) was the Acre-based Ottoman governor of Sidon Eyalet from 1776 until his death in 1804 and the simultaneous governor of Da ...
, besieged the castle, captured it and destroyed many of its remaining fortifications. The Galilee earthquake of 1837
The Galilee earthquake of 1837, often called the Safed earthquake, shook the Galilee on January 1 and is one of a number of moderate to large events that have occurred along the Dead Sea Transform (DST) fault system that marks the boundary of t ...
caused further damage to the structure and from then on the ruins were used as a quarry and a shelter for sheep. The late 19th century saw the start of study of Beaufort Castle, with surveys by Victor Guérin
Victor Guérin (15 September 1821 – 21 Septembe 1890) was a French intellectual, explorer and amateur archaeologist. He published books describing the geography, archeology and history of the areas he explored, which included Greece, Asia Mino ...
in 1880 and Claude Reignier Conder
Claude Reignier Conder (29 December 1848, Cheltenham – 16 February 1910, Cheltenham) was an English soldier, explorer and antiquarian. He was a great-great-grandson of Louis-François Roubiliac and grandson of editor and author Josiah Conder. ...
and Herbert Kitchener
Horatio Herbert Kitchener, 1st Earl Kitchener, (; 24 June 1850 – 5 June 1916) was a senior British Army officer and colonial administrator. Kitchener came to prominence for his imperial campaigns, his scorched earth policy against the Boers, h ...
in 1881 as part of the Survey of Western Palestine
The PEF Survey of Palestine was a series of surveys carried out by the Palestine Exploration Fund (PEF) between 1872 and 1877 for the Survey of Western Palestine and in 1880 for the Survey of Eastern Palestine. The survey was carried out after the ...
.
T E Lawrence
Thomas Edward Lawrence (16 August 1888 – 19 May 1935) was a British archaeologist, army officer, diplomat, and writer who became renowned for his role in the Arab Revolt (1916–1918) and the Sinai and Palestine Campaign (1915–1918 ...
visited the castle in 1909 during his walk across modern-day Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus li ...
and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, conducting research for his thesis. He was particularly struck by the view of the coast and along the Litani River
The Litani River ( ar, نهر الليطاني, Nahr al-Līṭānī), the classical Leontes ( grc-gre, Λέοντες, Léontes, lions), is an important water resource in southern Lebanon. The river rises in the fertile Beqaa Valley, west of B ...
.
In 1921 the French Mandate
The Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon (french: Mandat pour la Syrie et le Liban; ar, الانتداب الفرنسي على سوريا ولبنان, al-intidāb al-fransi 'ala suriya wa-lubnān) (1923−1946) was a League of Nations mandate foun ...
was established and French historians
This is a list of French historians limited to those with a biographical entry in either English or French Wikipedia. Major chroniclers, annalists, philosophers, or other writers are included, if they have important historical output. Names are lis ...
and archaeologists investigated the region's history and structures. The medieval historian began studying Crusader castles in the 1927 and his work influenced subsequent generations of historians of the Crusades. In 1936, seven years after he first visited Beaufort, Deschamps and architect Pierre Coupel organised 65 soldiers to clear Beaufort's inner enclosure and the keep
A keep (from the Middle English ''kype'') is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in c ...
. Kennedy highlights Deschamps' ''La Défense du Royaume de Jerusalem'' (1939) as a particularly important source in the study of Beaufort as "his descriptions and plans record a building which has probably been mutilated beyond recognition by recent military activity". The French Mandate ended in 1943 when Lebanon became independent.
The castle's strategic location, which affords a view of much of southern Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus li ...
and northern Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, has caused it to be a focus for recent conflicts. The Palestine Liberation Organization
The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO; ar, منظمة التحرير الفلسطينية, ') is a Palestinian nationalism, Palestinian nationalist political and militant organization founded in 1964 with the initial purpose of establ ...
(PLO) held the castle from 1976 onwards, during the Lebanese Civil War
The Lebanese Civil War ( ar, الحرب الأهلية اللبنانية, translit=Al-Ḥarb al-Ahliyyah al-Libnāniyyah) was a multifaceted armed conflict that took place from 1975 to 1990. It resulted in an estimated 120,000 fatalities a ...
and consequentially it was attacked dozens of times by Israeli
Israeli may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the State of Israel
* Israelis, citizens or permanent residents of the State of Israel
* Modern Hebrew, a language
* ''Israeli'' (newspaper), published from 2006 to 2008
* Guni Israeli ...
forces in the space of five years. On 6 June 1982, at the start of Operation Peace for Galilee (the 1982 Lebanon War), the PLO position on Beaufort Castle was heavily shelled by the Israelis before it was captured by the Israeli forces two days later in the Battle of the Beaufort. The fighting caused damage to the castle, and in the aftermath the Israeli army adapted the site for their own use by building a large forward operations base adjacent to the fort's western wall - as a result of prior presence of PLO and the fear of IEDs
An improvised explosive device (IED) is a bomb constructed and deployed in ways other than in conventional military action. It may be constructed of conventional military explosives, such as an artillery shell, attached to a detonating mecha ...
, Israeli soldiers manning the base were allowed to tour the upper floors of the fortress but prevented from accessing the lower parts. In 2000 the Israeli army left Beaufort, altogether demolishing the base. The IDF occupation of Beaufort provides the basis of the Israeli film ''Beaufort Beaufort may refer to:
People and titles
* Beaufort (surname)
* House of Beaufort, English nobility
* Duke of Beaufort (England), a title in the peerage of England
* Duke of Beaufort (France), a title in the French nobility
Places Polar regions ...
'', although the film itself was shot on the Golan Heights. After the Israeli withdrawal attempts by local tourism services to restore the fort began, albeit in very slow progress and lack of funding.
Construction
Several of the great Crusader castles were built on spurs, using natural defences and fortifying the one access point. The setting of Beaufort plays a role in the defence of the site, but the terrain is only impassable on the north side. The Kurds extended the castle to include a slightly lower shelf of rock immediately to the east of the castle, thereby removing one of the routes of attack. Divided into two wards, one occupying the lower ground to the east, the castle is roughly triangular in shape and measures about . Akeep
A keep (from the Middle English ''kype'') is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in c ...
or great tower was built against the west wall of the upper ward; the tower has a square plan and measures about . While it was common for keeps in Europe to be entered through the first floor, in Syria the convention was for a ground floor entrance as can be seen at Beaufort.Smail (1956), p. 227
References
Notes
Bibliography
* * * * * * *Further reading
* , London,p. 534
p. 535
* {{Authority control Castles in Lebanon Castles and fortifications of the Kingdom of Jerusalem Nabatieh Governorate Tourist attractions in Lebanon Castles and fortifications of the Knights Templar